Lido’s Roadmap to Pectra: Delivering Validator Consolidations in the Protocol [Pt 3]
Introduction
In the previous 'Lido's Roadmap to Pectra' explainer, we discussed how contributors to Lido DAO have been approaching the Ethereum protocol changes introduced by the Pectra hard fork (live since May 7 2025), particularly the opportunities and risks tied to EIP-7251, the major upgrade that raised MAX_EFFECTIVE_BALANCE limits for validators.
The article outlined three key areas of focus:
- Consolidation and large validator benefits and tradeoffs: Merging multiple 32-ETH validators into larger units reduces network load, and has a small positive impact on rewards. Effects on slashing and correlation risks are small, but response time becomes crucial to mitigate any losses.
- Modular upgrade: Any Lido protocol changes to support consolidations will be delivered through the Staking Router architecture, working towards a clean and safe deployment in line with the protocol's newest architecture.
- Phased rollout: Contributors are planning a careful and staged delivery of consolidations for the Lido protocol in Two Phases, starting with Lido V3, previewing more details to come on risks, scope, and release plans.
Balancing security, decentralization, and efficiency are key factors in shaping Ethereum’s staking landscape, and Lido will play a key role in scaling Ethereum. Today’s article discusses this commitment with a concrete plan to deliver the upgrade to all users of the Lido protocol.
Over the past months, Lido contributors have been exploring the opportunities and tradeoffs associated with validator consolidations, a concept unlocked by Ethereum’s latest upgrade, Pectra. The groundwork has been laid for some major protocol upgrades that stand to meaningfully improve the overall network while making the Lido protocol even more efficient and scalable.
Today we dive deep into understanding this evolution and how it reflects the long term vision for Lido, including the role the protocol will play in the future of Ethereum validation.
Once Lido v3 launches, the protocol will consist of two main parts: stVaults and Lido Core (which includes the Staking Router and its modules). stVaults will support 0x02-type large validators from day one, along with validator consolidations to a certain extent.
Lido Core, Large Validators & Consolidations
The Staking Router (SR) in Lido is a core architectural component that enables modular, and flexible Node Operator participation in the Lido staking protocol. It acts as the coordination layer in Lido Core, allocating staking deposits between the various modules that make up the core protocol. SRv2, launched in 2024, finally transitioned Lido from a monolithic, whitelisted operator set to its current modular architecture (which includes the Curated Module, SimpleDVT and Community Staking Module, plus any upcoming modules).
Staking Router v3
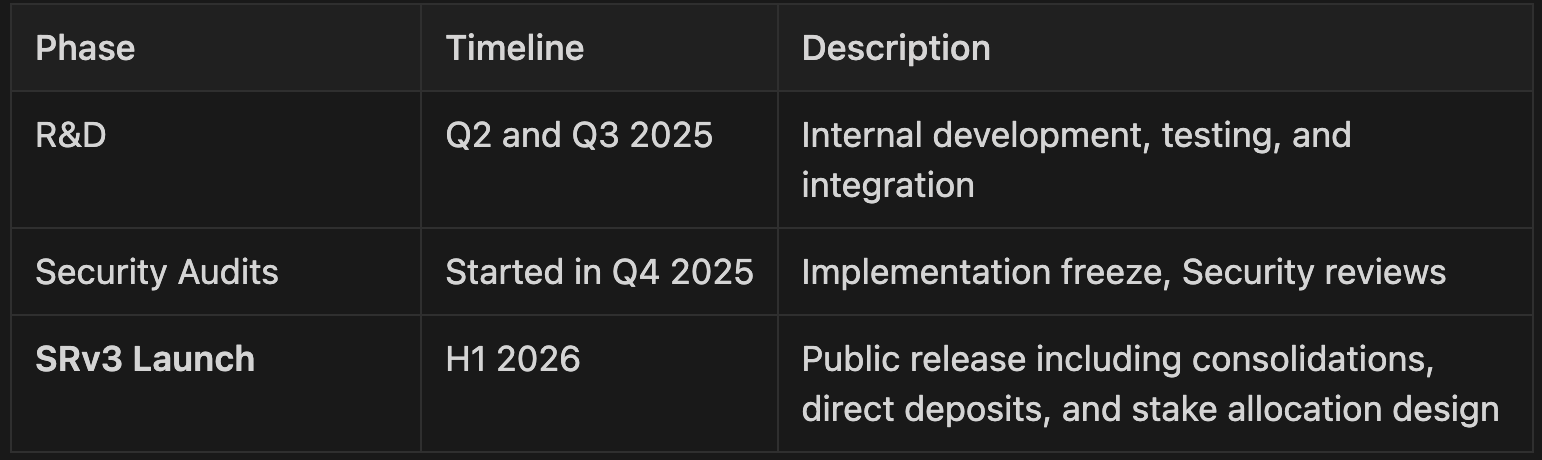
A new full-featured upgrade, dubbed Staking Router v3, is currently in development, and support for large validators and validator consolidations is expected to ship alongside it, in the first half of 2026.
SRv3 isn't just a minor update, it marks a significant step forward in the Lido DAO's commitment to Ethereum's long-term health and its benefits for the community. It reflects months of foundational design work and would act as a cornerstone release for the protocol's next phase. SRv3 is structured to serve multiple longer-term goals:
- Implementing a balance-based accounting system across the protocol, enabling modules to use either 0x01 or 0x02 validator types, and thus larger validators and validator consolidation.
- Enabling selective direct deposits at the module level, which compliments products such as the Distributed Validator Vault (DVV), ensuring that stake flows to validators that are run in a certain manner.
- Enabling stake reallocation between operators and/or modules through a combination of triggerable withdrawals, validator consolidations, and module direct deposit functionality.
- Laying the groundwork for marketplace functionality, a more granular architecture for SR stake allocation to be designed in tandem with other upcoming changes at the module level.
Staking Router v3 & What's Next
Why are consolidations so important?
Support for the new EIPs, including EIP-7251, is a key step in bringing Lido closer to Ethereum’s native validator mechanics, and it goes well beyond just letting operators consolidate their managed stake. While users might see some benefits like faster stETH redemptions, the real impact is deeper: it unlocks a more flexible and efficient protocol, technically and operationally.
With these changes, the protocol will be able to do things like:
- Reallocate stake between operators/modules with consolidation operations
- Support new deposits into large validators, naturally streamlining the network
- Lay the groundwork for smarter, leaner validator management overall
A new, 0x02-ready, accounting model: Although already supported by the stVaults architecture, this is a fundamental shift for Lido Core.
Currently, the Lido Protocol handles critical aspects of validator accounting (including functions such as: deposits, rewards, withdrawals, etc.) through a unit-based approach where 1 validator equals 32 ETH. A balance-based accounting model is absolutely crucial for consolidations because it allows the protocol to treat validators as flexible balances rather than fixed units, enabling seamless consolidation. For this to happen, a major rework of several key components of the on-chain protocol is necessary.
Consolidations via EasyTrack: This initial, optimistic and governance-driven implementation provides a secure and transparent way to operationalize consolidations, ensuring immediate utility for Node Operators.
By leveraging EasyTrack, an established and robust mechanism for regular protocol operations, the delivery of consolidations is significantly expedited. It can be implemented using Lido’s existing governance structure, significantly reducing the risks and operational overhead involved in the process.
Other Unlocked Features
As mentioned, SRv3 isn't just about unlocking consolidations. It also includes other vital components that lay the groundwork for Lido's future, including foundational support for Direct Deposits.
SRv3 will allow direct deposit support, which will streamline how new stake comes into the protocol and is allocated. This feature will initially be enabled at the module level (restricted to whitelisted actors), with the potential to become available for individual Node Operators within modules that support future allocation logic.
Groundwork for a New Stake Allocation Mechanism
These capabilities will enable the protocol to strategically optimize stake distribution based on defined parameters and performance metrics, a feature that has precedence in the protocol via CSMv2. Over time, the basic marketplace structure will support a more balanced and diversified validator set: reducing over-concentration, improving fault tolerance, increasing overall returns, and strengthening the resilience of the Lido protocol.
The Roadmap
The development plan for SRv3 reflects a clear set of priorities:
- Validator Consolidations: This is the top priority, ensuring effective and protocol-aligned rollout for operators.
- Direct Deposits: The next critical step to enhance stake inflow.
- Foundational stake allocation design: Essential for our long-term vision, expected to be designed alongside the SRv3.
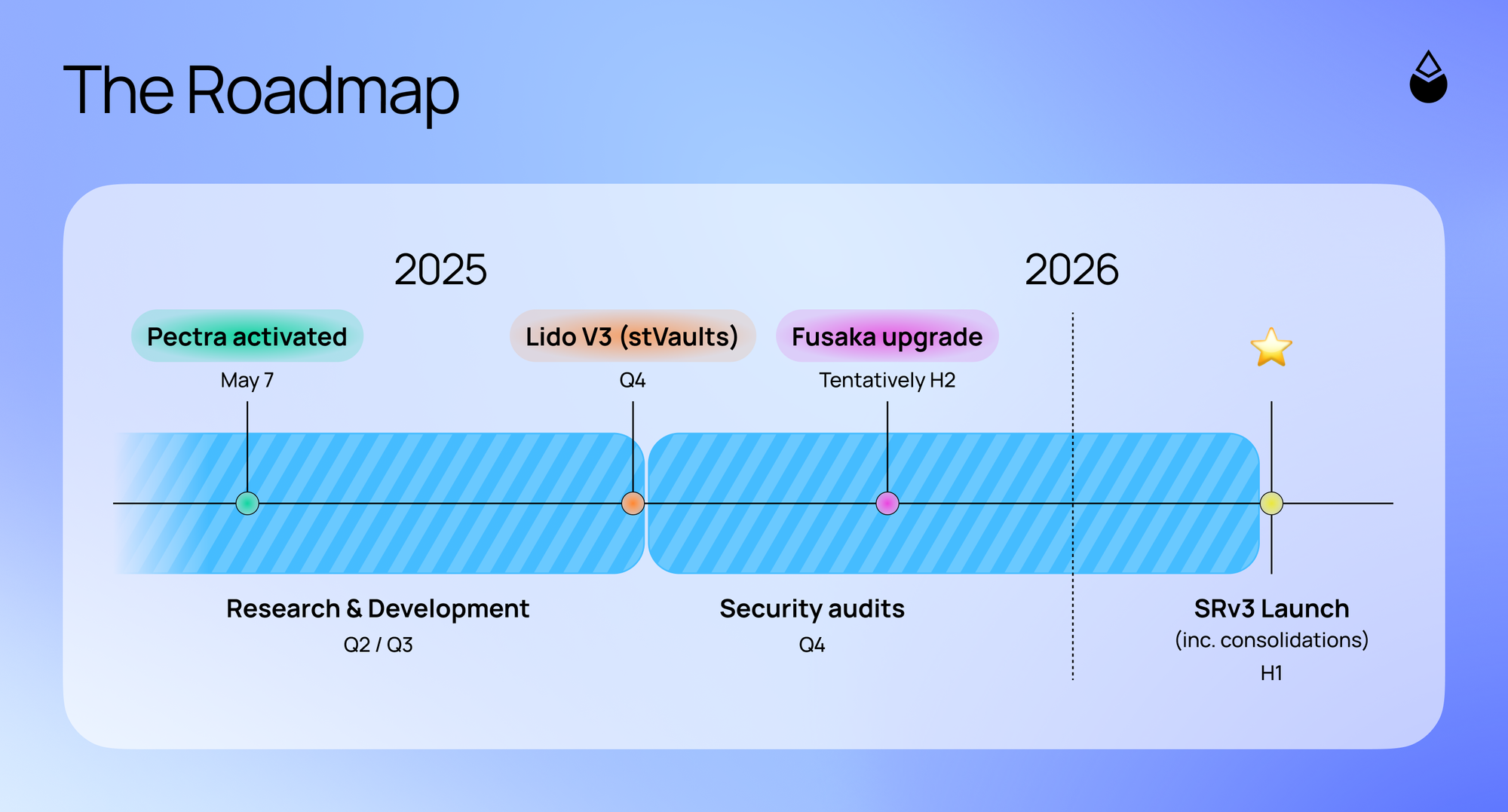
These upgrades are currently deep in research and development.
A Stronger, More Resilient Lido
The commitment to ship these upgrades in H1 2026, centered around Lido Core consolidations enabled by EIP-7251, reflects a coordinated effort across protocol stakeholders, driven by a shared focus on building a stronger, more resilient Lido.
These changes are expected to significantly improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the overall health of the protocol. Node Operators, in particular, stand to benefit from simplified management and lower overhead. This release marks another step in Lido’s ongoing commitment to innovation, decentralization, and delivering meaningful improvements across the ecosystem.
More updates will follow as the rollout of SRv3 progresses.